Theories of Meaning in Semantics | What is in the Meaning?
Introduction
Semantics, it is the branch of linguistics that deals with the meaning and manifestation of language. The term "semantics" is derived from the Greek noun "sema" which means 'sign or signal'. Broadly speaking, semantics is the study of the meaning of words or phrases, and the relation between referent and referend. The aim of semantics is, to find out how a man is able to understand the meaning, transform his ideas and why the surrounding changes the perspective of thinking the same knowledge in different ways.
The meaning is treated as the essence of language, and the speech without meaning has been called the tree without fruits and flowers. A speaker says a word to convey the message and he is concerned about how listeners understand the meaning of speech, because he wants a response and a listener doesn't get its meaning, and he cannot answer you. Theories of meaning are important to interpret the meaning of any speech or written text.
Semantics, it is the branch of linguistics that deals with the meaning and manifestation of language. The term "semantics" is derived from the Greek noun "sema" which means 'sign or signal'. Broadly speaking, semantics is the study of the meaning of words or phrases, and the relation between referent and referend. The aim of semantics is, to find out how a man is able to understand the meaning, transform his ideas and why the surrounding changes the perspective of thinking the same knowledge in different ways.
The meaning is treated as the essence of language, and the speech without meaning has been called the tree without fruits and flowers. A speaker says a word to convey the message and he is concerned about how listeners understand the meaning of speech, because he wants a response and a listener doesn't get its meaning, and he cannot answer you. Theories of meaning are important to interpret the meaning of any speech or written text.
The study of meaning is quite tough. Scholars have long puzzled over what words mean or what they represent, and how words are related to reality. A word has multiple meanings like the word 'table' dining table, round table and table of 2. So the context of a word is more responsible for its meaning. Numbers of scholars studied the "meaning". There are five theories of meaning in Semantics:
Five Theories of Meaning in Semantics
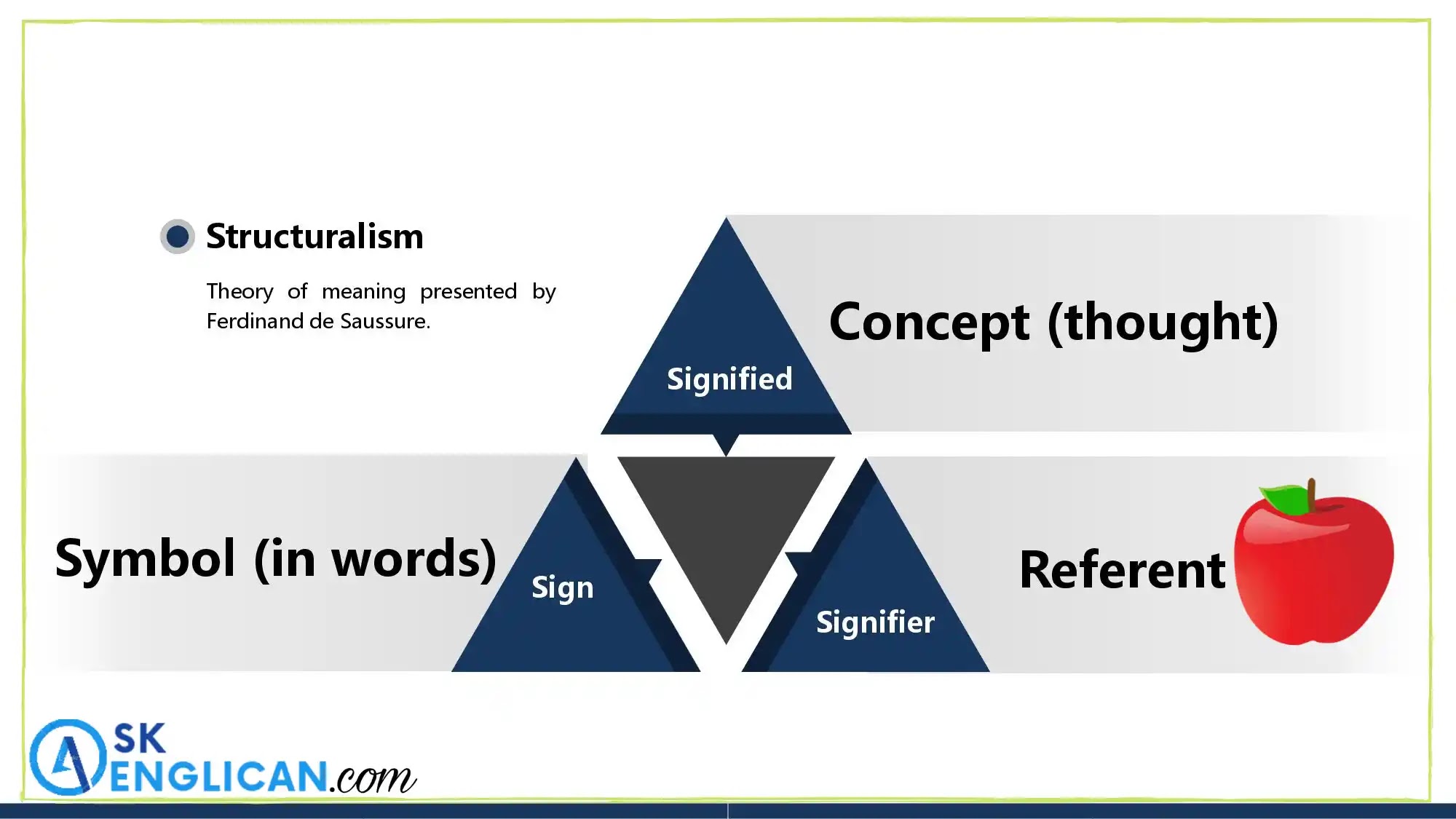
a - Structuralism
A Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure presented the theory of significance to explain the way in which the meaning is communicated. According to him words are related to each other as signs and can be struck together in various combinations to form sentences. He studied meaning in four dichotomies.
Sign, signifier and signified
Saussure held that language was a system of signs not words in general conversation would call these signs. In linguistics, a word points out certain objects and concepts. Distinct signs are different for phonemes or the meaning behind them. The study of signs is called semiotics. The sign has two components "signifier" the physical object of something and "signified" the sound image or concept.
Apple. 》sign
Physical image. 》signifier
Concept. 》signified
Apple. 》sign
Physical image. 》signifier
Concept. 》signified
- Di-chronic and Syn-chronic:
Linguists study the Di-chronic approach that language as it exists between two given points in time. Di-chronic linguistics is the study of the history of the evolution of language; the change of language from past to present. The synchronic approach studies the language as it exists at any given time. Synchronic (static) is a descriptive look at language at a certain point in time.- Paradigmatic and Syntagmatic:
Paradigmatic analyses the vertical change and composition of sentences.Like,
I go to Karachi.
He walks to school.
Syntagmatic analysis of the horizontal change and modification of sentences.
Like,
I like cricket.
He likes cricket rather than football.
- Langue and parole:
Two different aspects of language langue and parole. Langue refers to the language rules and conventions. According to Noam Chomsky language is the whole system of language rather than a single person's knowledge. Parole belongs to an individual when the convention exists in a mind.b - Seven types of meaning by Geoffrey Leech
Language is meant to communicate ideas, share knowledge, expressing thoughts and feelings to others. Furthermore, your keen interest is what he/she understood that you have spoken to him/her. But meanings exist in our minds and we can express what is in our minds through the spoken and written forms of language as well as through gestures, actions, signs, symbols, etc. Words, phrases and sentences have different meanings as well as multiple concepts but why? Geoffrey Leech studied the difference in decoding the meaning. He studied meanings into seven types or ingredients giving primacy to conceptual meaning.
- Conceptual/ Denotative meaning: It is the literal meaning of words found in the dictionary. Like, Needle: irony, a sharp instrument used for sewing. Most commonly it is known as conceptual meaning defines the exact concept of words.
- Connotative meaning: A speaker associates his personal meaning, it doesn't refer to the actual concept of the word but some features are found in it. Like, we associate qualities of something with the actual word. We call it lazy as a tortoise, tall as a giraffe.
- Social meaning: Influence of social speaker's background in conversation. Like, I ain't done nothing. Some American speakers use this.
- Emotive meaning: Words show the feelings, emotions and attitude of the speaker. Like, I hate you, get out of here. ( angry attitude)
- Reflective meaning: Words have multiple conceptual meanings and one replaces another strongly. Like, The poet could not but be gay. Previously, it was used as a happy person.
- Collocative meaning: Collection of words having the same meaning but each one is used in a different context. Like, She is a pretty girl. He is a handsome boy.
- Thematic meaning: Structuring the sentence to emphasize the word that is more important in a sentence. Like, Edison invented the bulb. The bulb was invented by Edison.
c - Bloomfield’s View of Meaning
Bloomfield (1933) stated that the context of the situation was an essential part of the meaning. A person interprets differently at age level. He described four stages of child development. As children grow older they understand differently than he gains any idea in the past. At an earlier age, he understands the meaning on the basis of material perspective, and at the age of 18, he gains abstract knowledge.
d - Sense and Referent
Meaning is the concept and the real-world representation of objects. A word can represent differently with the combination. Like, as a pen(used for writing etc.) I bought pens for Ali and Ahmed. Here pen is not denoting anyone. If I say, Ali's pen is better than Ahmed's pen. Generally, this combination changed the meaning of pen. Ali's pen and Ahmed's pen give different concepts and representations.
e - Theory of Meaning by Ogden and Richards
The "Theory of Meaning" is the concept that has been present in communication since the first humans learned to communicate. According to Craing Online, every word has a single correct meaning associated with it. So it can be seen that we cannot use a word twice to define any other thing.
Ogden and Richards claim with their theory, which states that there is not a single correct meaning associated with each word, simply meaning don't reside in words, meanings reside in people's mind. The meaning varies from person to person because everyone has different levels of understanding according to their standards, experiences, region, relation, etc.